is a key part of an online marketing strategy.
Maximum profit within a minimal investment!

SEO for stores and service sites
1. Evaluating the site
Tasks of optimizers
To effectively promote an e-commerce website, you need to:
- Conduct a thorough analysis of key competitors;
- Evaluate the volume of demand and seasonality of the topic;
- Analyze the current level of visibility and traffic;
- Realize the organic growth opportunities found.
SEO-optimization is a long-term and ongoing process that requires regular analysis and adjustments depending on changes in external and internal factors. Each stage of website promotion and optimization is important to achieve maximum results.
Find points of growth

Find growth points and assess the potential for traffic growth.
Analyze competitors, demand, seasonality, visibility and traffic.
Realize growth points

Rank the hypotheses of GP according to their potential for attracting traffic.
Implement an individual promotion strategy.
What kind of competitors are there?
When we analyze the market and niche in search of growth points, we think not only about the promoted site, but also about the competitors.
It is important to understand their varieties:
- indirect competitors
- direct competitors
It is your key competitors who have a significant impact on your sales that you should focus on. Analyzing and studying their strategies and tactics can be an important step to effectively plan and grow your business.
Direct competitors

Sellers of a similar product in the same market and serving the same target audience.
Indirect competitors

Companies selling different products but targeting your audience (channel displacers).
Features of E-commerce
Structured search engine snippets (prices, ratings, reviews) are the tip of the iceberg.
When competing for top positions, it is important to consider:
- The scale of the business;
- Proximity of resources;
- Age and indexation;
SE understands the size of the business and take these parameters into account in ranking sites.
Scale of business

Consider the scale of the business. It is not worth comparing large aggregators with startups, as the capabilities and ranking factors are different.
Nearby resources

If you are a small online store or aggregator it will be hard to beat companies that have a whole staff of programmers, content managers, etc.
Age and indexation
The graph of the average age of documents in the top search engine rendition is growing. This means that, on average, the sites in the top are getting older. The good news is that they age by exactly one year. There have been trends that the rendition has aged faster than a year for a year. In other words – the search engine was bringing up even older documents to the top, and this was a definite problem for the development of new projects.
Age plays an important role. A site with a 15-year history, all other things being equal, is difficult to overtake. Therefore, when analyzing competitors, it is important to take into account their scale in terms of the number of pages, traffic, niche capacity and other factors.
An increase in the age of documents at the Top of the search engine results indicates that established sites have an advantage in search results. This is because older sites usually have more time to accumulate authority, build backlinks and improve their reputation. These factors can contribute to better search engine rankings. Don’t be discouraged if your project is relatively new. It is important to take other factors into consideration when analyzing competitors.
How do we look for competitors?
In the case of determining competitors, we pay attention to a group of queries of a particular topic. The most important parameters are analyzed:
- Number of pages in the search engine index;
- The age of the domain;
- Number of links and donors;
- DR.
Often there is no point in looking at the whole topic, only at the competitors. For this purpose, we use visibility tools.
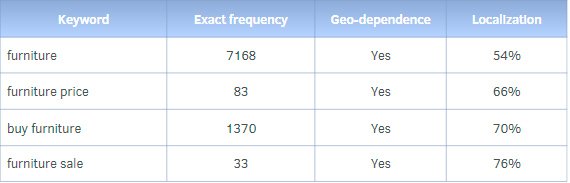
Query frequencies and geo-dependency
We give ~150 frequency search queries within some narrow topic. This could be “power chairs” or “computer desks” – competitors with maximum visibility in the topic are quickly identified.
How do we identify competitors?
Parameters X or DR can be calculated quite well in terms of traffic volume, thus identifying those competitors that are closest in age, total traffic, number of pages. We focus on the competitors who have very good visibility in the topic within this segmentation. We adopt their tricks for the promoted site, because the analysis of a successful competitor and the search for those hypotheses that have been implemented directly on it bring the greatest result.
Sites are defined as competitors if the semantic overlap with them is higher than 25%. If the overlap in semantics is low, there is no need to analyze them, because the promoted site simply does not compete with it. Thus, you can quickly understand which competitors are really competitors for you, and which sites can not be analyzed.
Example of competitor definition

For example, a site that sells household appliances does not compete with Amazon for the reason that there is little overlap in the volume of semantics.
2. Primary analysis
Evaluation of the project structure
Evaluating and optimizing these aspects of the project structure is important for user experience, search visibility and overall site effectiveness. When analyzing competitors, it is worth paying attention to their project structure and identifying opportunities to improve and optimize your own site.
What do we assess in this item?
- Sections: number, size, nesting or “linear” structure;
- Tags/marks: presence, number of levels;
- CNC: URL optimization and over-optimization, thoughtfulness;
- HRU: sections, subsections, product cards, tagged pages, etc.
The level of nesting of the site is also important for its effective organization. Well-structured sections, subsections and product cards make it easier for users to navigate and help them find the information they need quickly. Tagged pages also help classify and organize content, making it easier for users to find what they are looking for.
Example of structure assessment
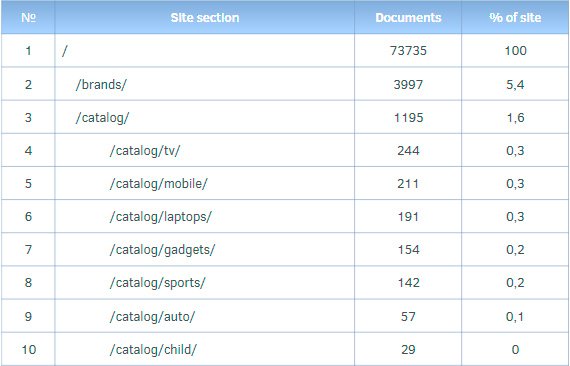
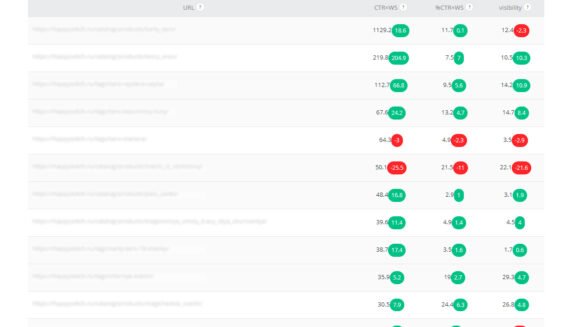
Estimation of current traffic volume
By estimating the current volume of traffic and understanding its sources, regions and behavioral characteristics, you can gain valuable insights into project performance.
What do we evaluate in this item?
- Traffic volume: dynamics and absolute size of the audience;
- Sources: search engines, advertising activity, etc..;
- Regions: cities and countries;
- Behavioral: average visit time, number of visits, etc.
This analysis allows you to identify areas for improvement, capitalize on successful traffic sources, and adapt your strategies to better meet the needs and preferences of your target audience.
Example of traffic volume estimation
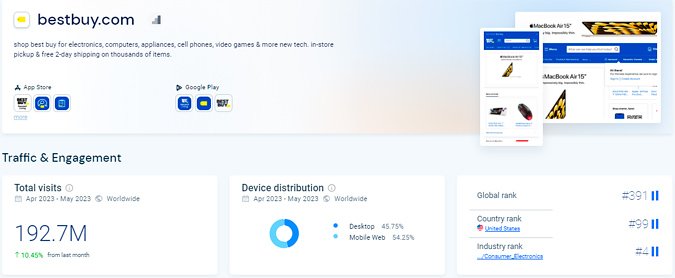
Regularly monitoring these metrics and comparing them to competitors’ results helps you stay competitive and adapt your marketing efforts effectively.
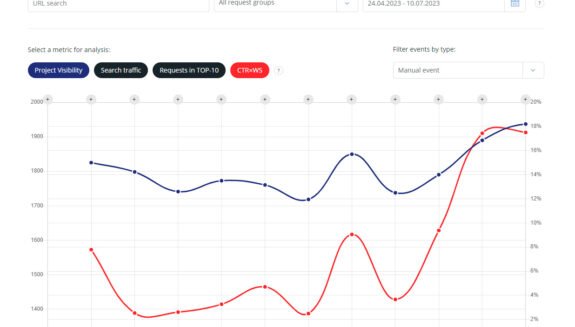
Traffic segmentation by potential
Segment key queries into groups to determine the potential for traffic growth. In terms of semantics groups, it is important to analyze the growth potential of each group of keywords.
How do we segment the traffic structure?
- By groups of key queries of the current traffic structure;
- By search engines and GEO to traffic growth potential;
- By groups of key queries to traffic growth potential.
When segmenting groups, you can see their growth potential as a percentage. Understanding this allows you to see the fundamental differences between the growth points of one group and another.
Segmentation of traffic structure and growth points
Growth points by URL group
This analysis prioritizes optimization efforts by comparing the current traffic volume to the growth potential of each URL group.
The following factors are taken into account:
- Current structure: regions, sections and segments attracting traffic;
- IP and GEO emphasis: potential by region for potential traffic;
- URL groups’ potential for growth: document sets, sections, cards.
By evaluating the current structure, highlighting search engines and geographic regions, and assessing the growth potential of URL groups, you can identify areas with the greatest potential for traffic growth. This analysis allows you to prioritize your optimization efforts, allocate resources efficiently, and focus on those areas that will have the most significant impact on increasing site traffic. Regularly monitoring these factors and adapting strategies accordingly will contribute to sustainable efficiency gains.
Example of growth points by URL group
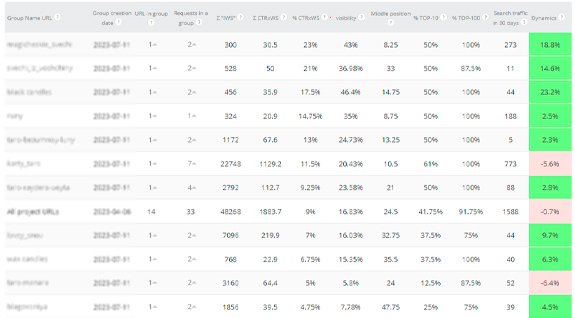
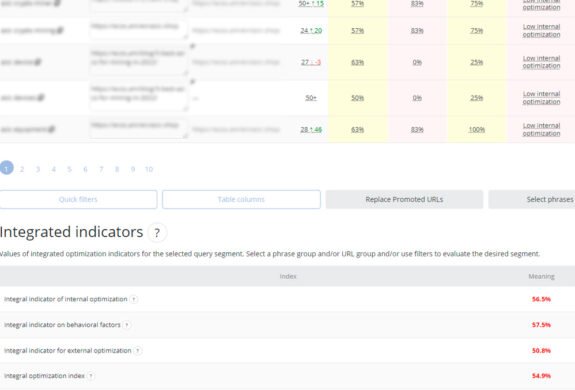
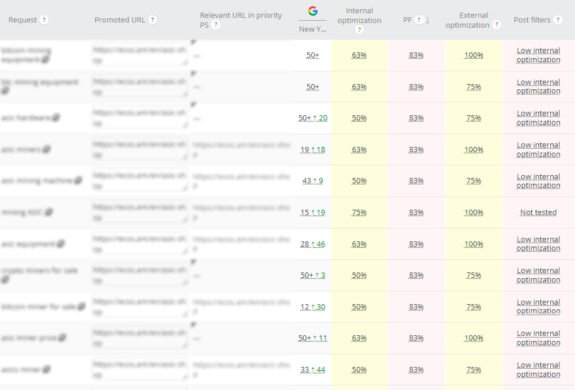
Degree of optimization
The degree of optimization is an assessment of the achieved level of optimization of the project taking into account various factors such as internal, external and behavioral parameters. These are taken into account by search engines in ranking (positions) for key site queries.
What do we evaluate in this item?
- Average optimization performance;
- Optimization for each query/URL;
- Over-spamming, post-filters and sanctions;
- Prioritize semantics.
By assessing the degree of optimization and considering internal, external and behavioral parameters, it is possible to identify areas that require further attention and improvement. This analysis allows you to optimize your project’s performance, increase search engine visibility and improve the overall user experience.
Integral relevance indicators
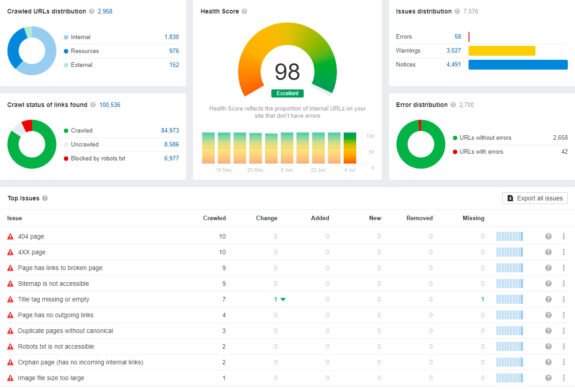
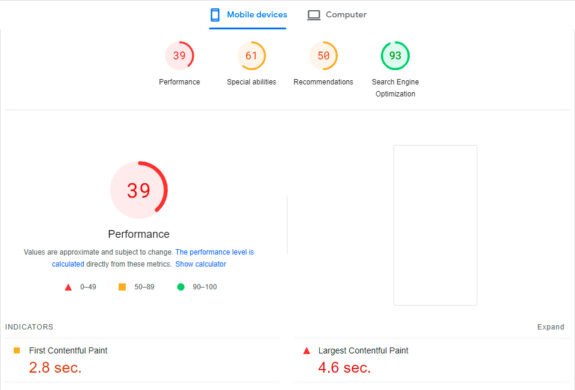
Technical errors and adaptation
Evaluating technical bugs and adaptations allows you to identify and fix problems that may hinder the performance and usability of the site.
What do we evaluate in this item?
- Crawler, webmaster panel, search output;
- Mobile adaptation;
- Loading speed: response up to – 200 ms, code loading time – up to 700 ms.
Working on technical bugs and customization plays a critical role in maintaining the health and performance of a website. It includes initial assessment and regular monitoring of the technical state of the site using various tools. Regular monitoring and proactive optimization ensure smooth site performance, usability across devices, and fast page loads. This not only increases user satisfaction, but also improves visibility in search engines and contributes to the overall success of the project.
Audit and control of technical parameters
3. Determining commercial demand
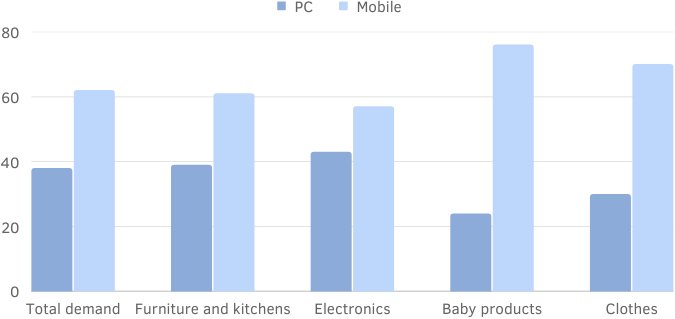
Mobile and desktop demand
Mobile and desktop demand is an important factor to consider when evaluating audience behavior and optimizing site performance. In many topics, the share of mobile demand exceeds 50%.
For example, in industries such as baby products, there is often a predominance of mobile demand. Moms often search for toys, hygiene products, and cribs using mobile devices. As a result, mobile traffic is prioritized and mobile-friendly sites are favored in search results.
In some cases, the ratio of mobile to desktop traffic can be as high as 80/20, while in other cases the difference may not be as noticeable.
Peculiarities of commercial demand
Category and card demand
Assessing the type of demand – categories (catalogs) or individual product cards (goods, services) – is very important because it provides insight into user behavior and preferences within specific topics or industries. They may have different levels of dominance in the demand for categories or cards.
The distribution of traffic between categories, tags, and product cards can vary depending on the topic. Analyzing groups of URLs allows you to quickly assess demand and understand the overall structure of traffic on the site.
By assessing the type of demand and analyzing groups of URLs, companies can gain insight into the growth potential of specific categories, cards, and brand pages.
Query group analytics
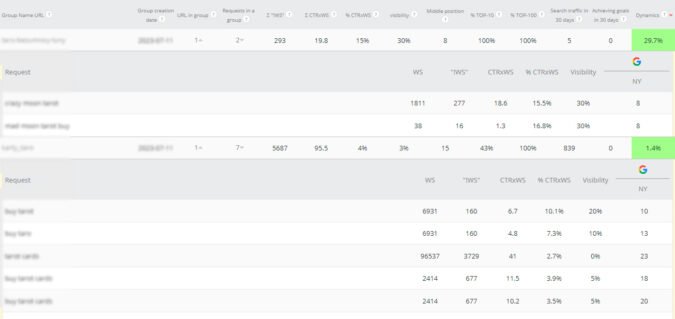
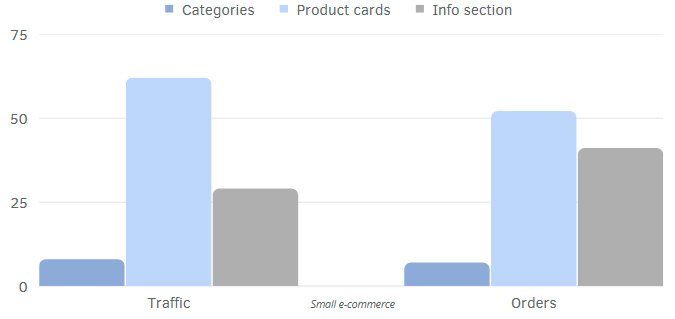
Traffic structure in ecommerce
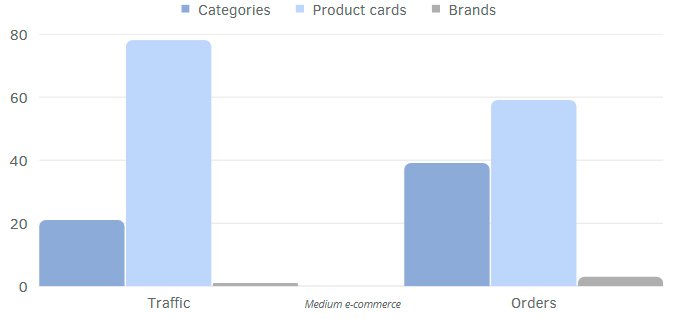
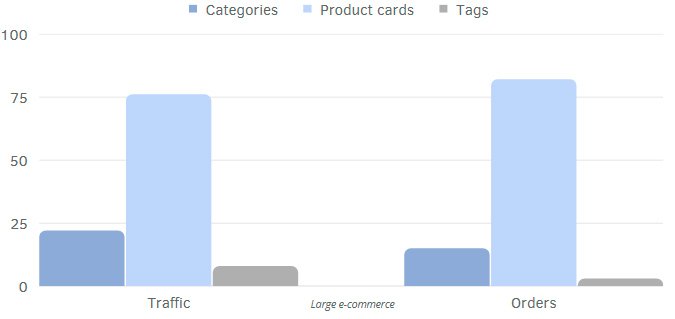
The structure of organic traffic to a website can vary significantly depending on the topic or area of business.
Organic traffic and order distribution examples for:
- Large e-commerce
- Medium e-commerce
- Small e-commerce
The distribution of traffic between page types can vary depending on a variety of factors. We identify unique traffic patterns and optimize elements to maximize the effectiveness of the strategy.
Examples of traffic distribution
Searching for points of growth
Comparing the metrics of attracted and potential traffic allows you to find and emphasize points of effort.
- Segmentation of categories into subgroups;
- Comparison of category and product potential;
- Determining the completeness of semantics development.
By comparing potential category and product traffic, assessing the completeness of semantic reach, and segmenting categories to optimize points, opportunities for growth can be identified. This analysis allows you to prioritize your efforts and focus on areas with the greatest potential impact.
Example of traffic growth points
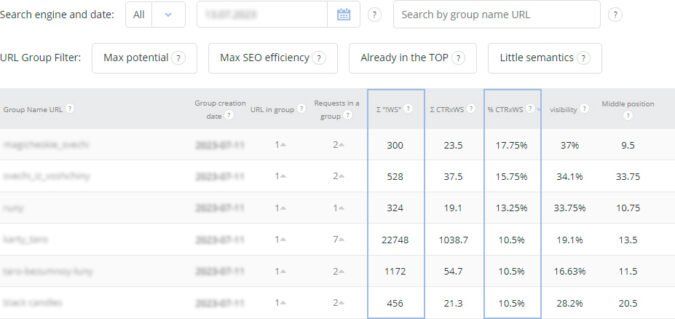
Domination

Determine what demand dominates the topic and the completeness of the semantic kernel.
Proportions

Determine average and current proportions of traffic structure: catalogs, product cards, etc.
Prioritization

We prioritize the semantic kernel based on margin data, CR and formulas.
By identifying the dominant demand, assessing the completeness of the semantic core, analyzing the proportions in the traffic structure and setting priorities for the semantic core, you can effectively optimize your site. This approach allows you to align your optimization strategy with the needs of your audience.
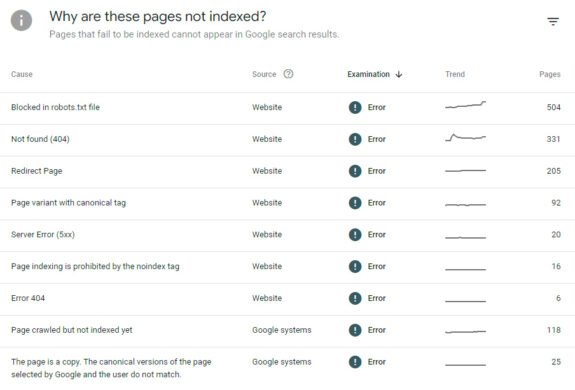
4. Search results analysis
Analysis of search results and semantics
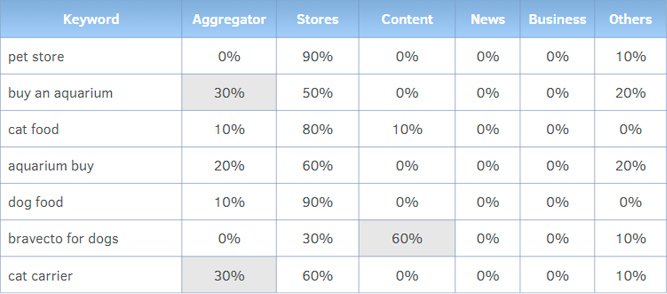
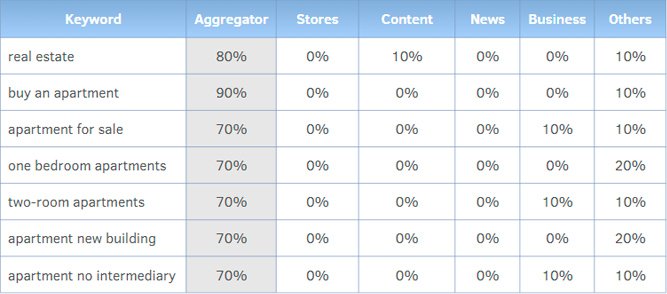
When analyzing search results, it’s important to note that some queries are dominated by aggregators, while others are dominated by online stores or other types of sites.
For example, if you search for the query “pet store”, the search results may show mostly online stores, while aggregators are absent. Conversely, for a query such as “buy an aquarium” or “buy an apartment”, aggregators may be present in significant numbers.
This highlights the importance of evaluating what types of sites appear in search results for keyword queries, and which ones should be prioritized for optimization.
Not all queries are equally useful
SERP evaluation by site type
Understanding the composition of search results helps you identify key players in a particular industry or topic. By analyzing the sites that consistently appear in search results, you can gain insight into their strategy, strengths, and competitive positioning. This information can inform decision-making and inform your own optimization strategies.
The composition of SERPs can change over time, reflecting changes in user behavior and search engine algorithms. Observing changes in the popularity of different types of sites can provide valuable insights into new trends and developments in the digital landscape.
Types of resources
- Aggregators
- Online stores
- Businesses
- Content
- News
- Video
- Services
Understanding SERP performance by site type provides insight into the diverse ecosystem of online resources and the competition for visibility across industries. By being proactive and adapting, companies can capitalize on opportunities, leverage new types of sites, and create unique experiences that capture the attention and engagement of their target audience.
User Intent Evaluation
Analyzing user intent is one of the important aspects of understanding the search landscape. By evaluating intents, we gain insight into the needs and desires of searchers.
Variations in user intent:
- Commercial outcomes
- Photos and videos
- Maps and travel
- Dictionaries
- Reviews
Example of intent definition
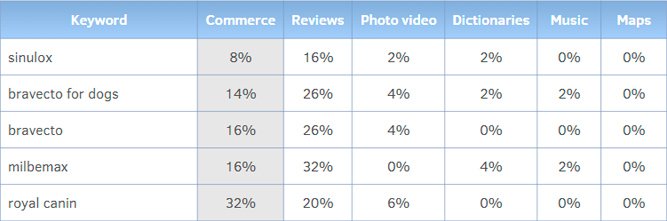
Understanding the intent behind users’ search queries allows us to provide relevant and valuable services that meet users’ desires and goals.
Keyword filtering
Filtering keywords based on intent, map priority, individual infocluster and SERP composition allows you to refine your online store optimization strategy and align it with the specific needs and preferences of your target audience. This approach ensures that your efforts are focused on attracting and converting relevant traffic, which will increase the visibility and effectiveness of your online store.
By digging deeper into the filtering process, online retailers can uncover interesting market dynamics, capitalize on niche opportunities, and refine their strategies to improve customer acquisition and retention.
By intents

- Commercial
- Prioritize card-based
- Separate info cluster
By SERP composition

- Less than 5-7 aggregators
- There are stores in the Top 3
- Direct competitors in SERP
5. Optimize by ranking factors
Main ranking factors
Behavioral

Attendance, region, engagement, CTR in SERPs, etc.
Commercial

Purchase function, prices, filtering, assortment, ordering options, etc.
Technical

Adaptive layout, loading speed, SSL certificate, etc.
Internal

Inclusion of the query in document zones – meta tags, internal links, etc.
Taking into account and optimizing these key ranking factors allows online stores to increase their visibility, attract relevant traffic and increase conversion rates. Monitoring, analysis and adjustments based on performance indicators and user feedback contribute to continuous improvement and long-term success in the competitive marketplace.
Store Optimization Zones
Optimizing an online store involves focusing on different areas of the store in order to increase its visibility, relevance and user-friendliness. The key areas of optimization are title and meta tags, headers, breadcrumbs, surrounding text, product titles and descriptions, menu category names, filters, additional information in the sidebar, alt and title attributes of images, and displaying the number of products.
Taking these aspects into account when optimizing store listing areas allows online stores to create a visually appealing, personalized and customer-centric shopping environment. Constantly seeking innovative approaches and incorporating these elements into an optimization strategy helps online stores stay competitive, delight customers and ensure long-term success in the dynamic world of e-commerce.
Apart from the mentioned optimization areas, online store owners should consider the importance of user-generated content (UGC) and social proof in their optimization strategy. Encouraging customers to leave reviews, ratings and testimonials about their purchases can have a significant impact on the decision-making process of potential customers.
List of optimization zones
- Title and meta tags;
- H1-H6 headings;
- Breadcrumbs;
- Pre- and post-listing text;
- Product titles and descriptions;
- Menus: category titles;
- Filters: occurrence in elements;
- Additional information in sidebar;
- Alt and title attributes of illustrations;
- Quantity of goods.
Groups of factors of critical importance
Critical importance
- Matching the type of the promoted page
- Presence of optimized Title tag
- Presence of prices
- Availability of “Buy/Order” functionality
- Presence of adaptive version of the site
- Large assortment of goods and services
- Presence of contact page
- Document loading speed of the mobile version
Importance of the 1st priority
- Information about availability/unavailability
- Filtering functionality
- Sorting functionality
- Availability of “Shopping cart” functionality
- Availability of quality text on the page
- Presence of city number
- Presence of regional visits
- Average CTR of a snippet
Importance of the 2nd priority
- Site size – number of pages in the index
- Age of the site in the eyes of the search engine
- Average page load time
- Presence of viewport meta tag
- Word occurrences from promoted phrases
- Presence of structured text on the page
- Presence of configured HTTPS protocol
- And many others
These factors play a crucial role in optimization efforts. Taking them into account allows online stores to improve visibility, functionality and user experience, which ultimately contributes to success in the competitive online marketplace.
Audit of ranking factors
Checking the site for compliance with ranking factors is carried out by manual and automated methods. A comprehensive audit (on average) contains 50 sheets.
A ranking factor audit is a critical evaluation process to identify strengths, weaknesses, and areas for improvement in terms of search engine optimization (SEO).
The audit looks at key areas such as on-page optimization, technical SEO, backlink profile, user experience, content evaluation, local SEO factors, etc.
A combination of manual and mechanized analysis provides insight into overall site condition and areas of focus.
Integral relevance indicators
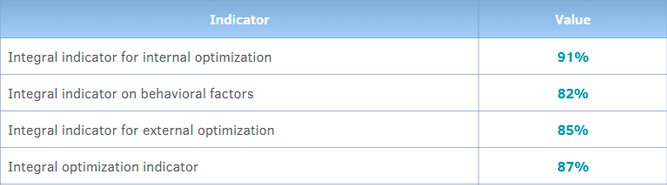
Manual analysis involves human expertise and attention to detail, while automated tools help identify potential problems and provide data-driven analysis. In addition, an audit opens up the opportunity to uncover hidden potential and discover untapped optimization opportunities. It allows you to go beyond basic SEO practices and explore innovative strategies to gain competitive advantage.
6. Increase conversion rate
Funnel and key metrics
When optimizing a website, it is very important to consider the sales funnel and understand the different stages of the customer journey. This will help to determine the type of conversions to track and measure the effectiveness of marketing efforts.
The main stages of the sales funnel:
- Reach (shows): channels, CA, CPM
- Traffic (conversions): CTR, CPC
- Engagement: CR, CPA
- Purchases: C1, CAC
- LTV
Sales funnel metrics
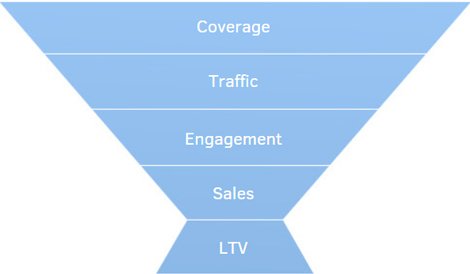
Types of entry points and types of conversions
When dealing with listing or tag pages, the main objective is to entice and engage users by showcasing a product card that piques their interest. The purpose of a listing page is not to make a direct sale, but to direct users to relevant product cards.
The main task of a product card is to convince the user to make a purchase. This emphasizes the importance of building trust in the store, providing transparent information about delivery, payment options, prices and other important details. The roles of these two elements on the user journey and their respective optimization allow online stores to improve the overall shopping experience, increase conversion rates and increase loyalty.
Listings and tags

Objectives:
- Retention
- Engagement
- Product comparison
Product cards

Objectives:
- Conversion to purchase
- Trust in the store
- Price, delivery and payment
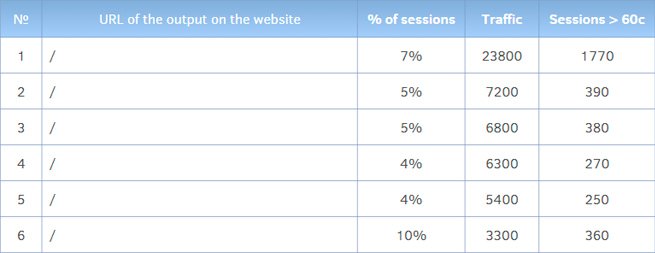
Working out exit points from the site
Analyzing exit points from a website in terms of conversions is very important to identify areas for improvement. Using automated tools and statistical systems, data can be collected on pages with low engagement and short session duration. These metrics indicate potential problems with traffic retention on these pages, giving you the opportunity to optimize them to improve performance and increase revenue for your company.
Implementing A/B testing or user feedback mechanisms can provide additional insights and validate the effectiveness of optimization activities.
Automated URL search by parameters
Optimization of EEAT factors
In YMYL (Your Money or Your Life) topics, analyzing and improving EEAT (Expertise, Experience, Authoritativeness, Trustworthiness) metrics is critical.
Expertise
Expertise: Evaluates the level of knowledge, expertise and skill demonstrated on a web page or site. Google looks for accurate, well-researched content that contains valuable insights from experts in the field.
Experience
Experience: the value of content created from personal experience. By considering the element of experience, search engines can provide more meaningful, interesting and accurate content that reflects real-life experiences.
Authoritativeness
Authoritativeness: This assesses the reputation and authority of a content author or website. Google considers factors such as the author’s experience, industry recognition, and overall credibility of the site when determining the authority on a particular topic.
Trustworthiness
Trustworthiness: Reliability and trustworthiness of information. Transparency, indication of source, absence of misleading content or deceptive practices, compliance with legal and ethical norms, have an impact on credibility.
Ranking products in the listing for maximum benefit
CTR
The challenge of listing: user retention
The conversion rate for traffic that is accounted for by listings is usually 2- times lower than the conversion rate of traffic that is accounted for by product cards.
CR
Once you go to an item, it must be purchased
The probabilities of conversion of this product/service card, after the transition. Those goods for which each click on this product is more realistic.
Profit
Margin on sale of goods / profit
Those products for which you will make more money as a business with each click.
* depending on how well the ranking is currently set up.
Listing to the hub
Transforming listings (categories) into a hub:
- Links to categories and subcategories;
- Attractive text and headings;
- Easy sorting and filtering;
- Popular products and brands;
- Guides, reviews, articles;
- Reviews and ratings;
- Navigation.

Converting a category to a hub can significantly increase conversion rates, turning it from a standard page into a comprehensive document that contains all the information you need.
This transformation allows users to not only browse popular products, but also access additional information.
In situations where buyers are having difficulty making a decision, addressing their other needs within the ad can significantly increase conversion rates.
* depending on the site parameters.
Cases of search engine promotion
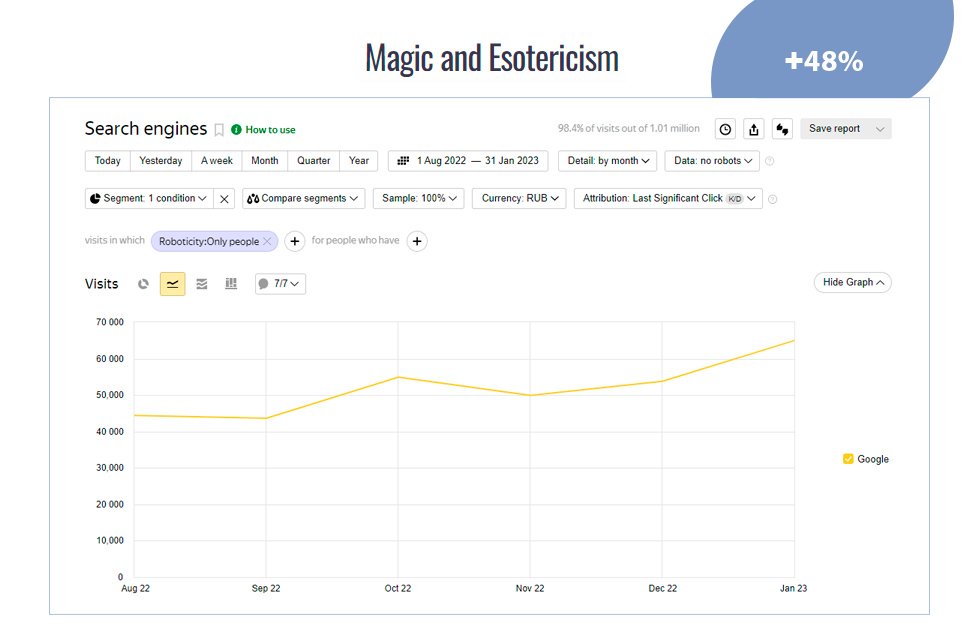
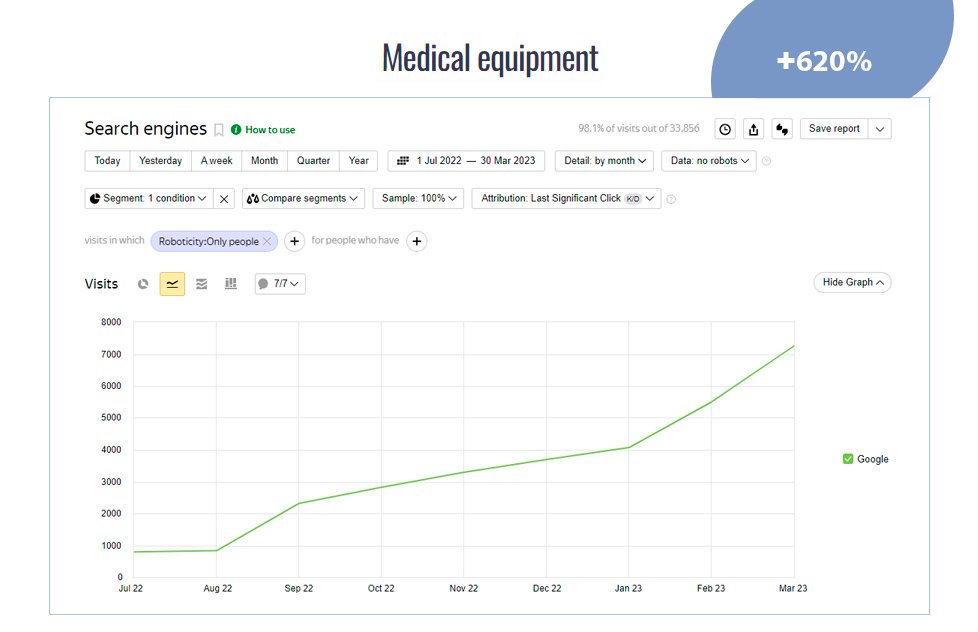
Easy and fast start of SEO work
Month 1
Audit and strategy
Comprehensive site audit, clustering, structuring, identifying organic traffic growth points.
Month 2
Optimization
Creating material, adjusting optimization zones, implementing edits on promotion strategy.
Month 3
Promotion
Create material, adjust optimization zones, capture results, and iterate successful growth points.